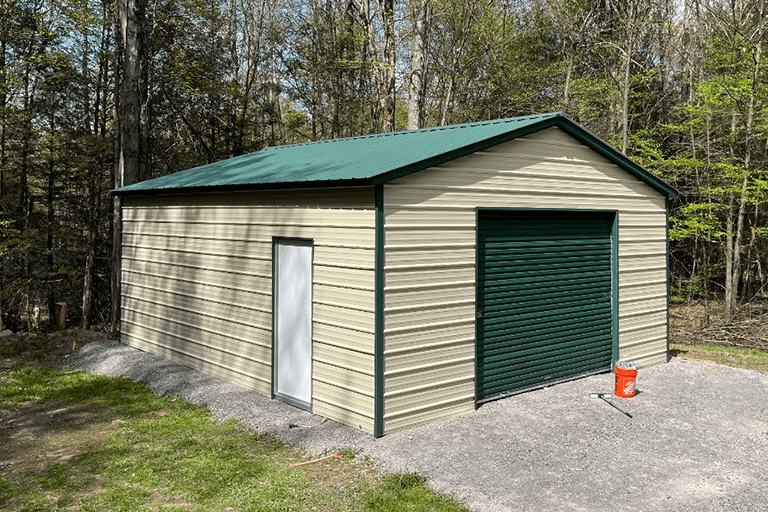
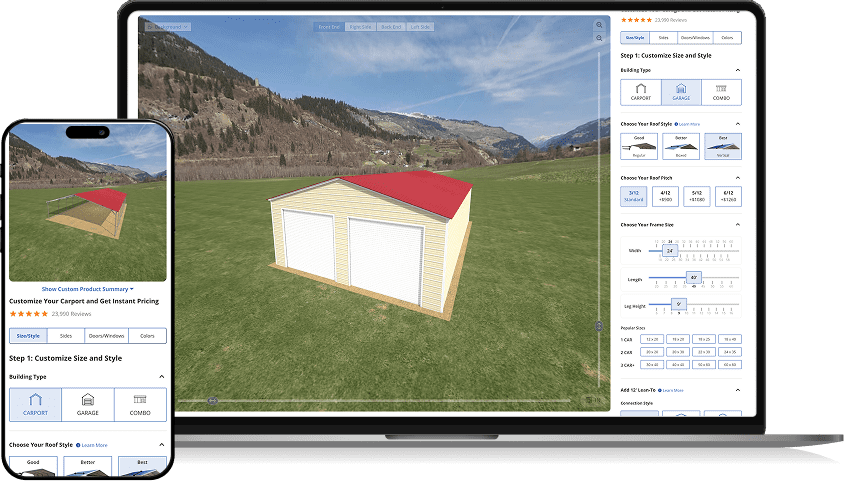
A tool shed is a standalone structure built for organized storage and light-to-moderate workspace needs. Compared to a general garden shed or outdoor storage shed, a tool shed typically prioritizes tool organization, security, and durability, especially if you store power equipment or want a small work area.
A tool shed can take a messy garage corner and turn it into a clean, dedicated spot for projects and storage. Instead of tripping over garden tools, extension cords, and lawn equipment, you get a place for everything, plus a work surface when you need it. Homeowners use an outdoor storage shed for woodworking, metalwork, seasonal items, and everyday overflow. A sturdy, heavy-duty shed with lockable doors also helps protect expensive equipment from weather and opportunistic theft.
This guide covers the decisions that matter most: practical sizes, materials, sample layouts, ventilation, lighting, and foundation options. You’ll also see example floor plans and layout ideas that make it easier to plan a garden shed or workshop shed that actually works for how you use your space.
Ways to Use a Tool Shed
Here are a few common ways people use a tool shed day to day:
- Storing garden tools. Keep rakes, shovels, pruners, and soil amendments organized and off the patio.
- Parking lawn equipment. Store a mower, string trimmer, fuel cans, and attachments in one dedicated spot.
- Organizing woodworking tools. Create zones for a small bench, clamps, and portable saws without taking over the garage.
Tool Shed Sizes and Dimensions
Tool shed sizing comes down to two things: what you want to store and how you want to move inside the shed. Some homeowners plan by square footage, while others think in cu. ft and shelving capacity. Either way, measuring your largest items first (like lawn equipment or riding mowers) prevents buying a shed that feels cramped on day one.
A simple approach is mapping your “must-store” items, then adding room for future storage space and a basic layout. Even a small shed feels bigger when the door swing, aisle width, and shelf placement match how you actually work.
Here’s a quick, practical guide to what common sizes can hold:
- 6×8 or 8×8. Store hand tools, garden tools, a small push mower, and a couple of shelving runs.
- 8×10 or 10×10. Fit larger lawn equipment, longer wall storage, and enough open floor to turn and carry items safely.
- 10×12 or 10×16. Store bulkier gear, add a workbench wall, and keep a clearer center aisle for easy access.
Small Tool Sheds (Under 80 sq. ft.)
Small sheds work best when you treat the walls like your primary storage system. Using vertical shelving, hooks, and tall cabinets keeps the floor open and makes a tight footprint feel more usable.
Here are a few ways to maximize space without adding clutter:
- Using vertical shelving. Keep frequently used garden tools off the floor and easy to grab.
- Hanging tools on hooks. Store long-handled garden tools neatly without blocking walkways.
- Adding a slim pegboard. Organize small items for everyday tool storage in one visible spot.
If you need a garden tool shed for weekend yardwork, a resin storage shed often makes sense because it’s lightweight, quick to assemble, and easy to keep clean.
Medium Tool Sheds (80–150 sq. ft.)
Medium sheds are the sweet spot for many homeowners because they can store equipment and still leave room to work. This is where a tool shed starts functioning like a small shop, especially if you add a compact storage cabinet system and a dedicated bench wall.
Here are a few features that improve day-to-day usability:
- Adding a storage cabinet. Keep small parts, hand tools, and supplies organized by category.
- Reserving a bench wall. Create a consistent workspace without moving items around each time.
- Choosing a double door. Make it easier to bring in and out bulky items without scraping the frame.
If you plan to roll in a lawn mower and stack bins, outdoor tool sheds with a double door make moving equipment much easier.
Large Tool Sheds (150+ sq. ft.)
Large sheds can handle true workshop setups, including tool walls, larger benches, and open space for projects. This size is also where electrical setups start to make sense, such as overhead lighting, multiple outlets, or a dedicated circuit for bigger tools.
Here are a few planning priorities that keep larger spaces functional:
- Planning clear zones. Separate storage, work areas, and equipment parking for smoother workflow.
- Upgrading lighting. Add brighter overhead lighting for safer cutting, drilling, and detailed tasks.
- Improving ventilation. Support comfort and airflow, especially if you run tools or store chemicals.
A heavy-duty metal tool shed can be a strong fit for workshop sheds in harsher climates because steel construction holds up well against pests and many weather conditions. Plan ventilation early, and think through window placement if you want a tool shed with windows for daylight and airflow.
Choosing the Right Size for Your Needs
Choosing the right shed size depends on how you plan to use the space now and in the future. Smaller sheds prioritize organization, medium sheds balance storage and access, and larger sheds support full workshop setups. Planning ahead helps prevent outgrowing a tool shed and keeps the space practical as your needs change.
Tool Shed Materials to Choose From
Material choice affects durability, upkeep, and how well a shed handles pests and moisture. In humid areas, rust resistance and ventilation matter more; in sunny climates, UV exposure becomes a bigger concern for finishes and plastics.
Steel Tool Sheds
Steel sheds offer superior strength and security, making them a good choice for long-term tool storage in harsher climates. A heavy-duty option like galvanized steel provides strong weather resistance and added protection against the elements and physical damage. Galvanized steel construction resists corrosion better than untreated metal, and it pairs well with reinforced locking mechanisms and roof designs that shed water effectively.
Looking for a durable, secure storage solution? Explore metal sheds at Alan’s Factory Outlet to find customizable options built to handle tough weather and protect your tools year-round.
Wooden Tool Sheds
Wood sheds offer a classic look and can feel warmer inside, which many people prefer for woodworking. Wood also supports easy customization, like adding extra wall blocking for cabinets or mounting heavier storage systems.
The tradeoff is maintenance. Keeping wood protected usually means staying on top of paint or stain, watching for moisture issues, and checking for pests so tool storage stays clean and dry.
Resin & Plastic Tool Sheds
A resin storage shed is popular for low-maintenance outdoor storage shed needs. Many resin options are UV-resistant, so they hold color and resist cracking better in sunny conditions than cheaper plastics.
Resin also tends to be lighter than wood or metal, which can simplify assembly and placement. It works especially well for basic storage, small yards, and homeowners who want a clean look without ongoing refinishing.
Tool Shed Layouts and Floor Plans
A good tool shed layout makes the space feel bigger than it is. The goal is creating clear zones — work, storage, and access — so you do not constantly shuffle items around to reach what you need.
If you are searching for 10×10 tool shed plans, start by reserving one wall for long storage, one wall for shelves, and keeping a clean center aisle. That simple approach works for garden tools, power tools, and combo use while protecting usable storage space.
Woodworking Layout Example
A woodworking layout often works best with a central workbench and wall storage around the perimeter. Place shelving and cabinets on one long wall, hang clamps and hand tools on the other, and keep lumber vertical in a corner rack.
The pros are a clear workflow and easy access to tools. The con is dust, so planning ventilation matters more than it does in a simple storage shed, especially if you run saws or sanders in workshop sheds. Put a window near the bench for daylight, and use zoning to keep finishing supplies separate from cutting tools.
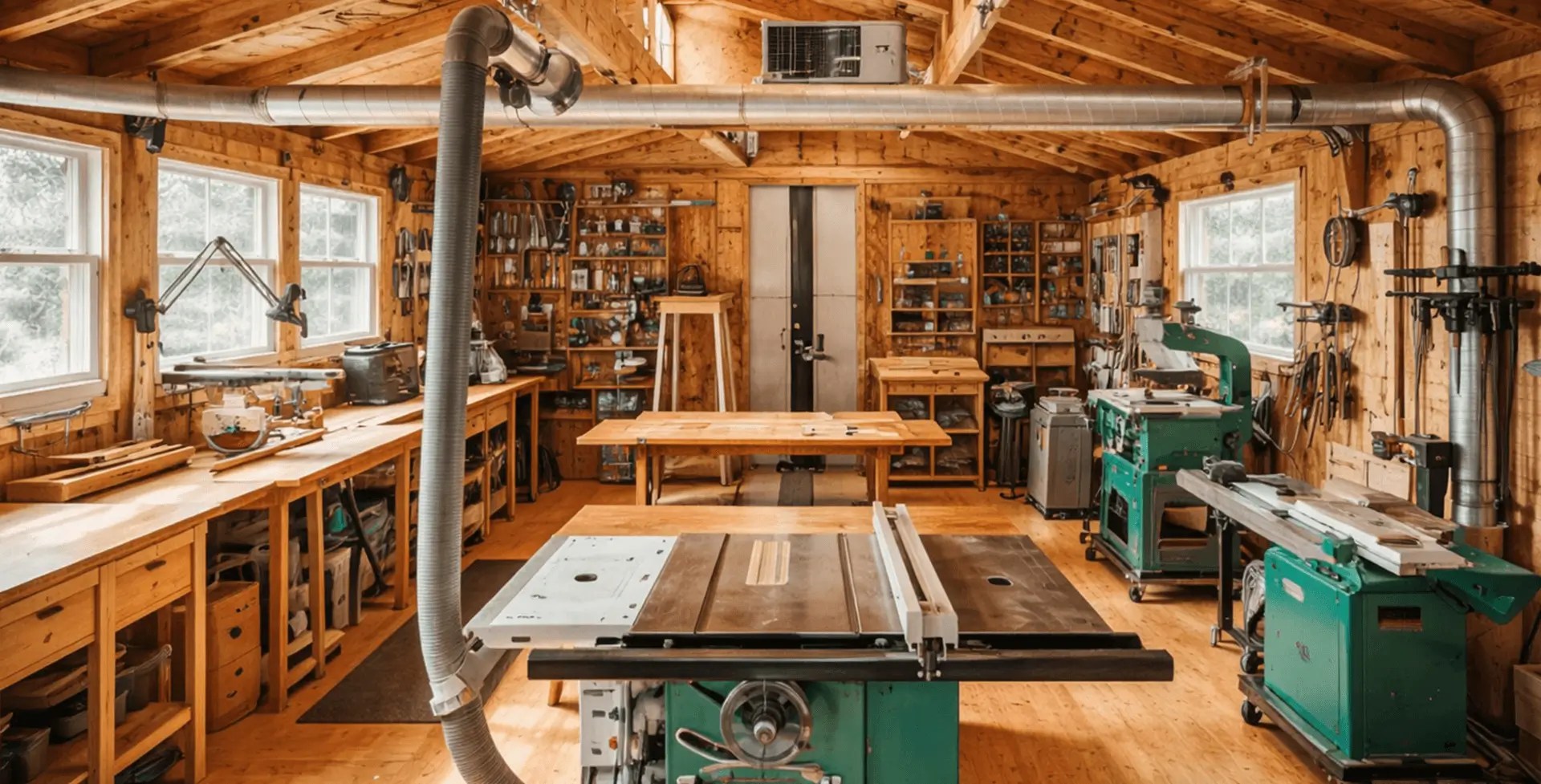

Gardening Layout Example
A gardening-focused setup is all about vertical storage and quick grab-and-go access. Use wall-mounted racks for rakes and shovels, add a slim shelf for small hand tools, and keep a clear floor strip for bins and bags.
The pros are easy organization and faster cleanup after yardwork. The con is moisture and dirt buildup, so plan a simple cleaning routine and keep frequently used garden tools near the door if you use the shed daily. A small potting bench along a side wall works well, especially if you add a hook strip above it for gloves and pruning tools.
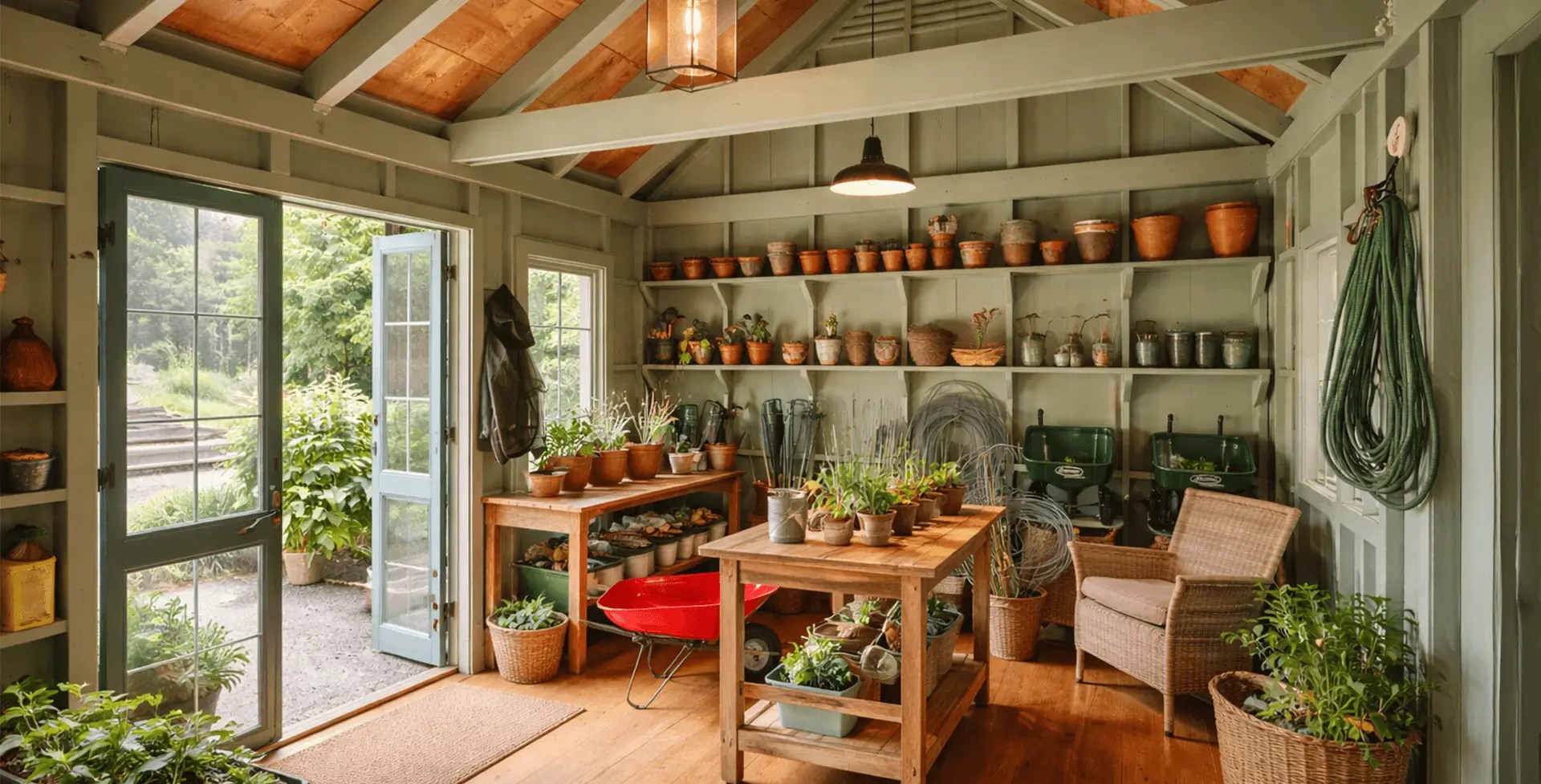

Combo Layout Example
A combo layout supports both storage and a small workspace, which is ideal if you do light repairs, weekend projects, and yardwork. Put shelves on one side, a compact bench on the other, and reserve the back wall for long items like ladders or spare lumber.
The pros are flexibility and less clutter in the garage. The con is crowding if you overschedule the same space, so plan limits for what lives inside full-time. For equipment access, a double door makes loading easier, and lockable doors support secure storage, especially for heavy-duty tools or fuel-powered equipment.
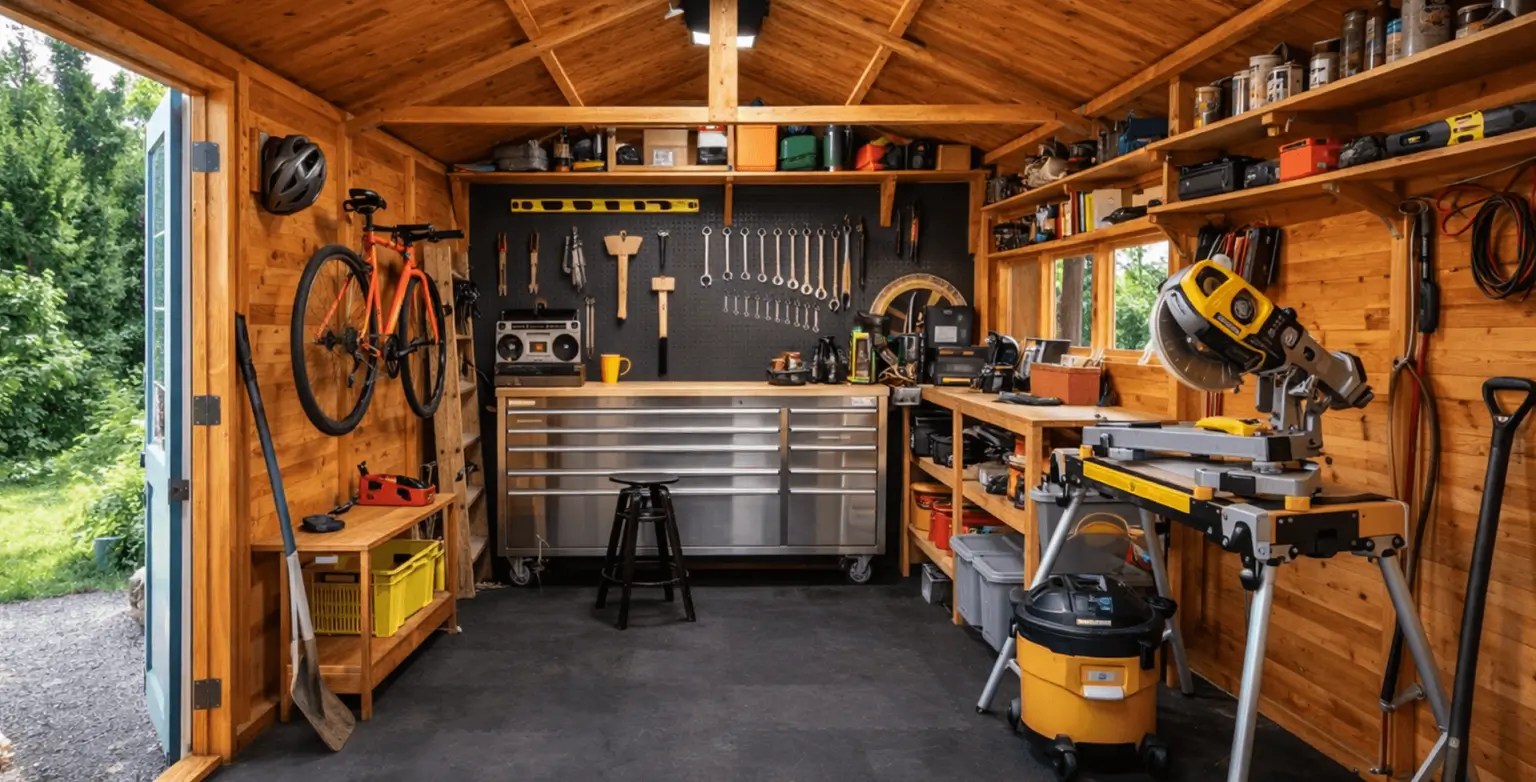

Foundation Types for Tool Sheds
Your foundation affects leveling, drainage, and how well your shed holds up over time. A simple rule is picking the best foundation for a tool shed based on what stays level, moves water away, and matches the weight of the structure and what you plan to store.
Below is a quick pros-and-cons comparison of common shed foundations:
| Tool Shed Foundations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Foundation type | Pros | Cons |
| Gravel pad | Promotes drainage and helps keep the shed floor drier | Needs careful leveling and a border to prevent spreading |
| Concrete slab | Provides a flat, long-lasting base for heavier sheds and equipment | Costs more and takes more prep time |
| Wood platform | Works well on slightly uneven ground and supports airflow under the shed | Needs ongoing checks for moisture and rot risk |
No matter which option you choose, plan for water moving away from the shed. That means grading, gutters if needed, and keeping the area around the shed clear so the structure stays weather-resistant over the long run.
How to Build or Install a Tool Shed
Most sheds follow the same basic setup process, whether you buy a prefab kit or take a DIY approach. The main difference is how much framing and finishing you do yourself versus assembling panels and hardware from a kit.
Here’s a step-by-step guide you can use for a tool shed or outdoor storage shed install:
- Clear and level the site. Remove sod, check slope, and confirm you have room for doors and setbacks.
- Build the foundation. Install a gravel pad, pour a concrete slab, or construct a wood platform based on shed weight and site conditions.
- Assemble the structure. Build framing or assemble panels, then square the walls before securing the roof.
- Install doors and seal gaps. Add door hardware, weather sealing, and trim so water stays out around corners and openings.
- Plan the roof runoff. A sloping roof helps shed water, and a lean-to design can work well in tight side-yard locations if local rules allow it.
When You May Need a Permit for a Tool Shed
Permit rules depend on your state, county, and city, and they often vary based on size, height, and intended use. Even when a permit is not required, you may still need to follow zoning rules like setbacks and lot coverage.
Many places use a size threshold as a starting point (often cited around 120 sq. ft. or higher), but rules can differ, and HOAs can require approvals regardless of shed size. Utility hookups like electricity or plumbing also typically trigger permits and inspections.
If you live in a historic district or flood zone, check early. It is easier to adjust a shed location on paper than after a foundation is in place.
Choosing the Right Tool Shed for Your Property
Start with your site limits. Measure available yard space, confirm setbacks from property lines, and think through access paths so you can move equipment without fighting tight corners.
Climate should steer material choice. In wet or coastal areas, a metal garden shed with corrosion-resistant construction and good ventilation can help, while hot sun makes UV performance more important for resin materials.
Also consider how custom you want to go. Prefabricated sheds install faster, semi-custom options let you choose doors and windows, and fully custom builds can match very specific workshop needs. If you are considering an upgrade to a larger steel structure that functions more like a garage-style workshop, price out your options through the 3D Carport & Metal Garage Builder at Alan’s Factory Outlet.
Create Your Functional Workspace
A tool shed works best when you plan it like a small room, not a dumping zone. Pick a size that leaves an aisle, choose materials that match your climate, and set up zones for storage and work so the shed stays useful over time.
If you want a metal tool shed or outdoor storage shed that supports real projects, consider upgrades like better lighting, added vents, and a layout that keeps daily-use items within arm’s reach. Explore Alan’s Factory Outlet today for customizable shed options that help you build a functional, long-lasting workspace. We offer free delivery and installation in our 21-state service area.
Free Delivery and Installation in 21 States

FAQs for Tool Sheds and Workshops
If you are narrowing down a shed choice, the small details usually matter most. These quick answers cover common questions homeowners ask while planning tool storage, layouts, and everyday use.
Is it cheaper to buy a shed or have one built?
Buying a prefab tool shed is often cheaper than building from scratch because you reduce labor time and avoid multiple material runs. Custom builds can make sense if you need a very specific footprint or finish, but they often cost more once you factor in framing, roofing, and labor.
Material matters here, too. A metal tool shed can offer long-term durability for many climates, while an outdoor storage shed made from resin may cost less up front for simple storage needs.
What tools should I keep in a tool shed?
The right tool list depends on what you do most often. A good baseline includes items for yardwork, basic repairs, and project cleanup, then expands for hobbies like carpentry, metalwork, or working on cars.
Here are useful categories to stock based on common use cases:
- Garden tools. Store rakes, shovels, pruners, gloves, and a hose setup for seasonal work.
- Lawn equipment. Keep a mower, string trimmer, fuel container, and spare line or blades in one zone.
- Project basics. Organize a drill, fasteners, measuring tools, a level, and extension cords for quick fixes.
Can I store garbage cans or patio furniture in a tool shed?
Yes, a tool shed can protect a garbage can from wind, animals, and weather, especially if the doors seal well. A larger outdoor storage shed can also hold patio furniture seasonally, as long as you keep cushions dry and maintain airflow with vents or windows.
The main caution is space creep. The more bulky items you store, the less room you have for tools and using the space as a work shed, especially if you are trying to keep an outdoor metal storage shed organized for projects.
What’s the difference between a tool shed and a garden storage shed?
A tool shed focuses on tool organization, security, and workshop-style use, such as storing power tools and creating a small bench area. A garden storage shed is a specialized version that usually prioritizes gardening supplies, including soil, pots, fertilizers, and hand tools.
Match the shed type to your available space and focus on layout and shelving that supports your routines, whether that means quick access to garden tools or a dedicated tool shed setup for weekend projects.