If you’re planning to remodel or add a structure to your home, it’s essential to know which building materials to use.
The most common materials for home additions—like patios, carports, and detached garages—include steel, wood, brick, and concrete. Depending on factors such as location and design, some may be better suited than others.
In this guide, we’ll discuss each option in depth and introduce new alternative options to consider when choosing the best building materials for your property.
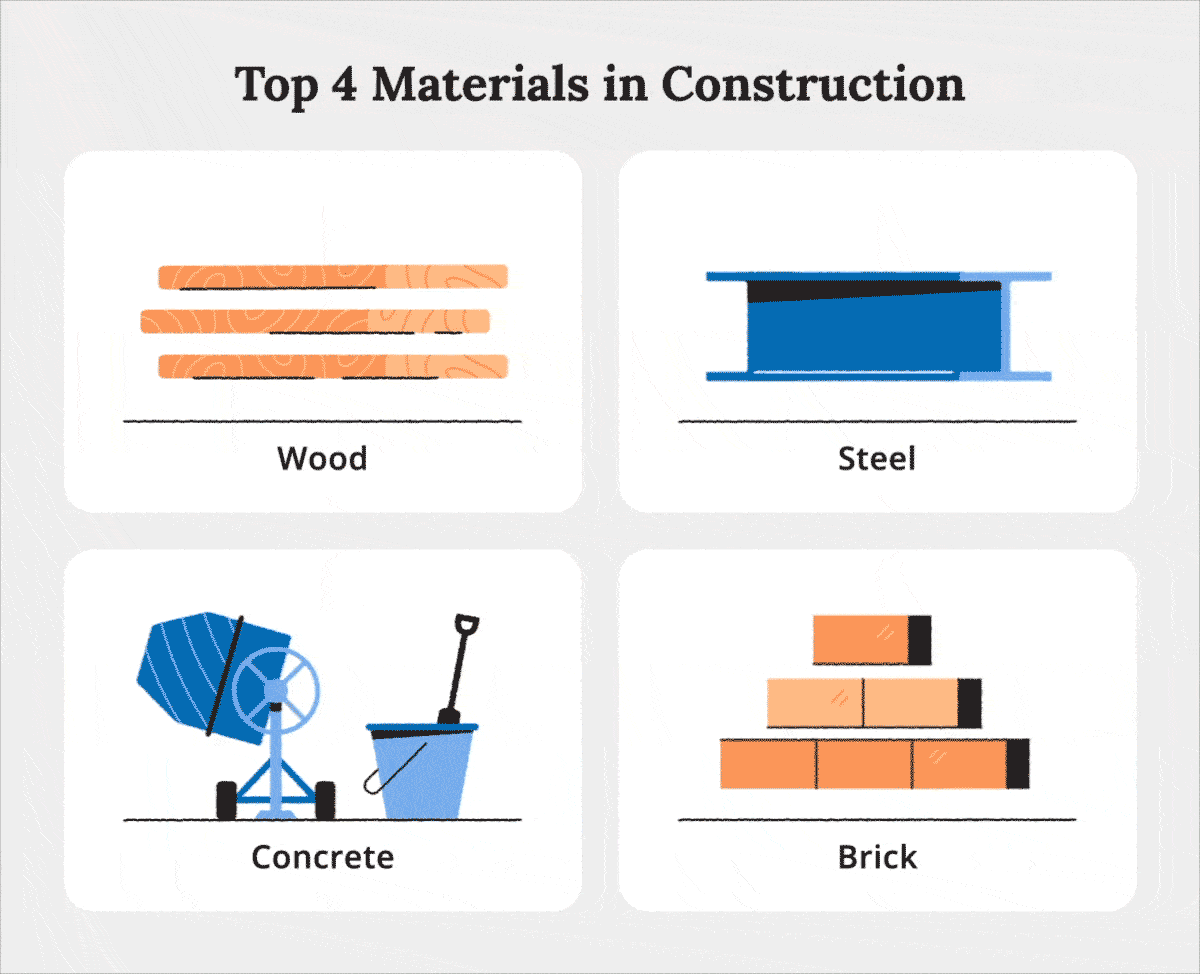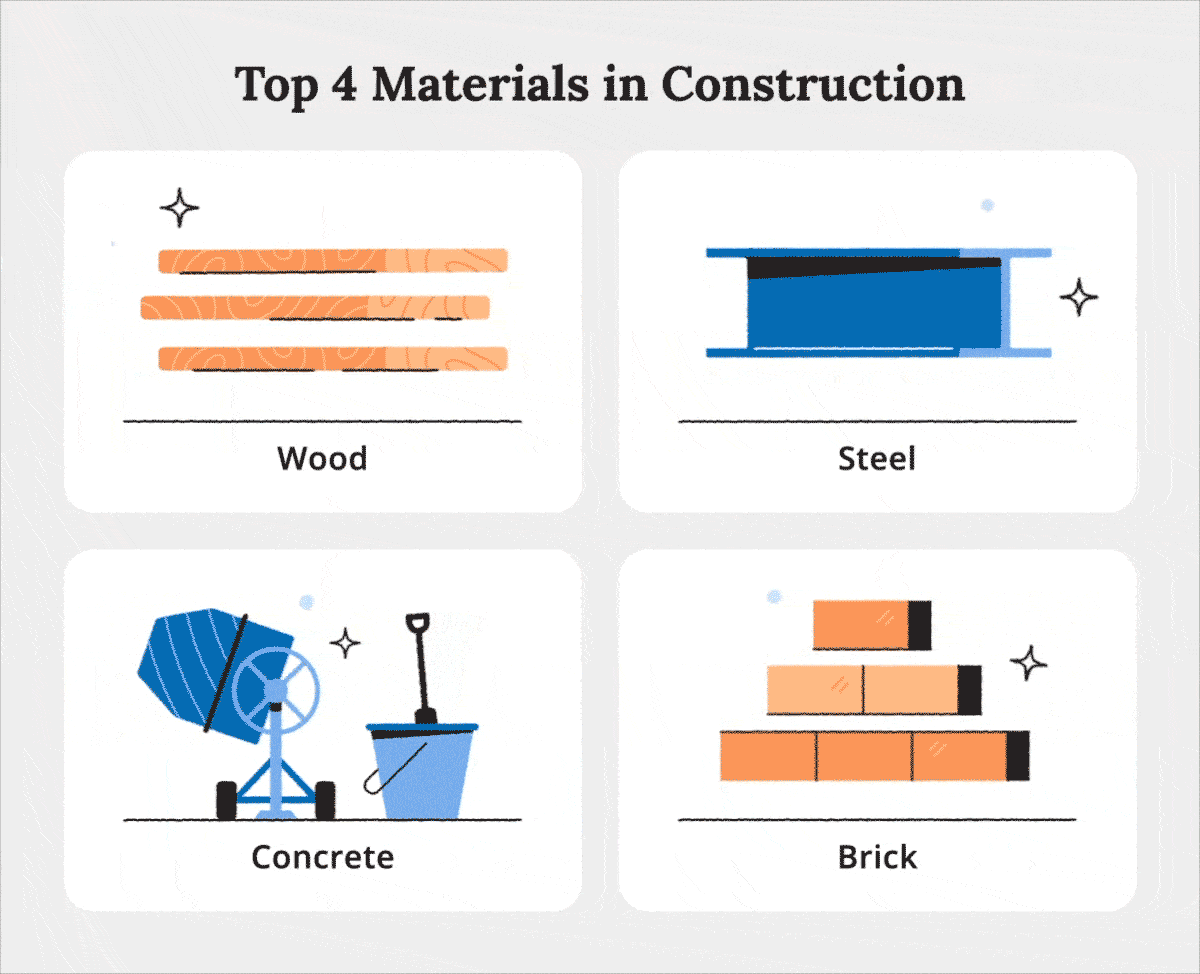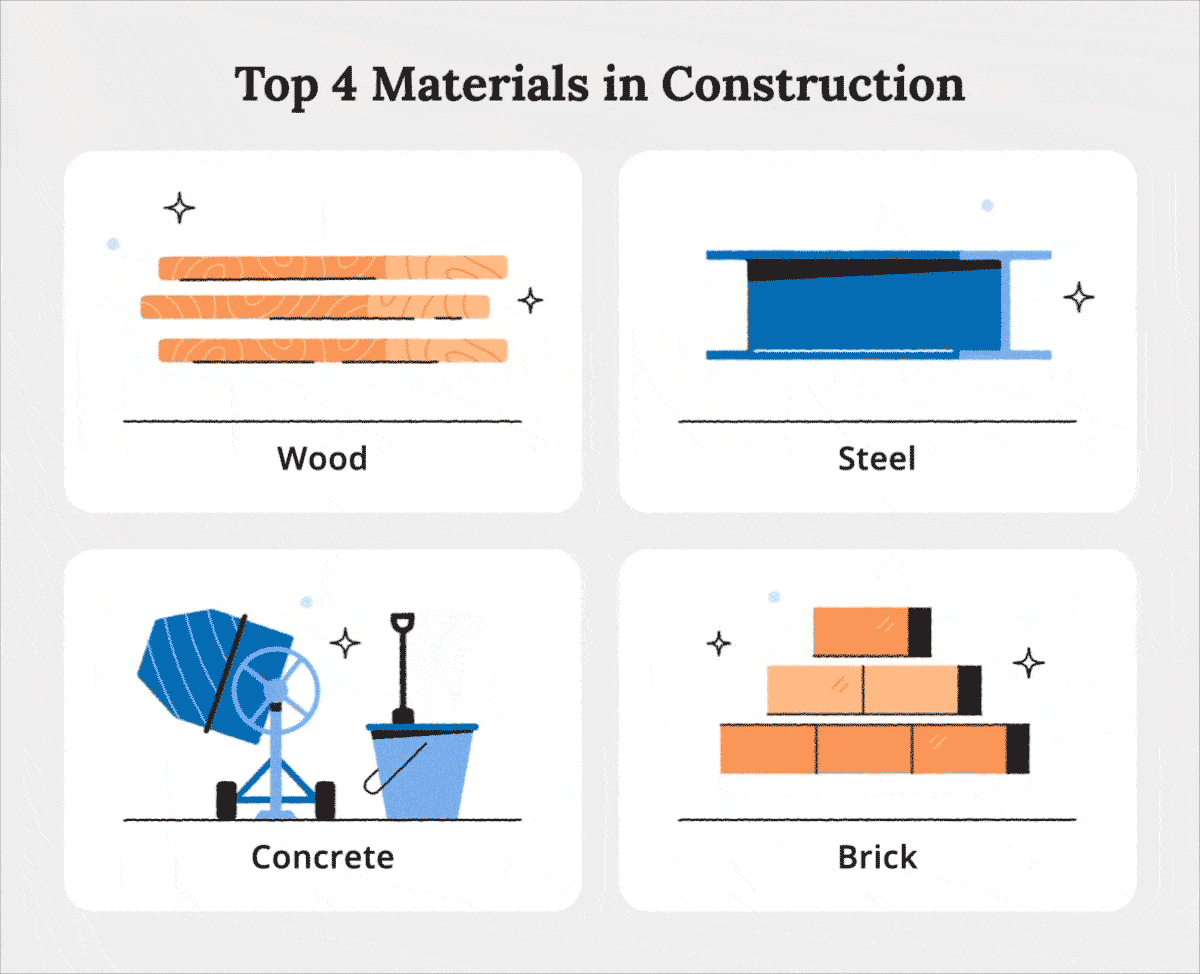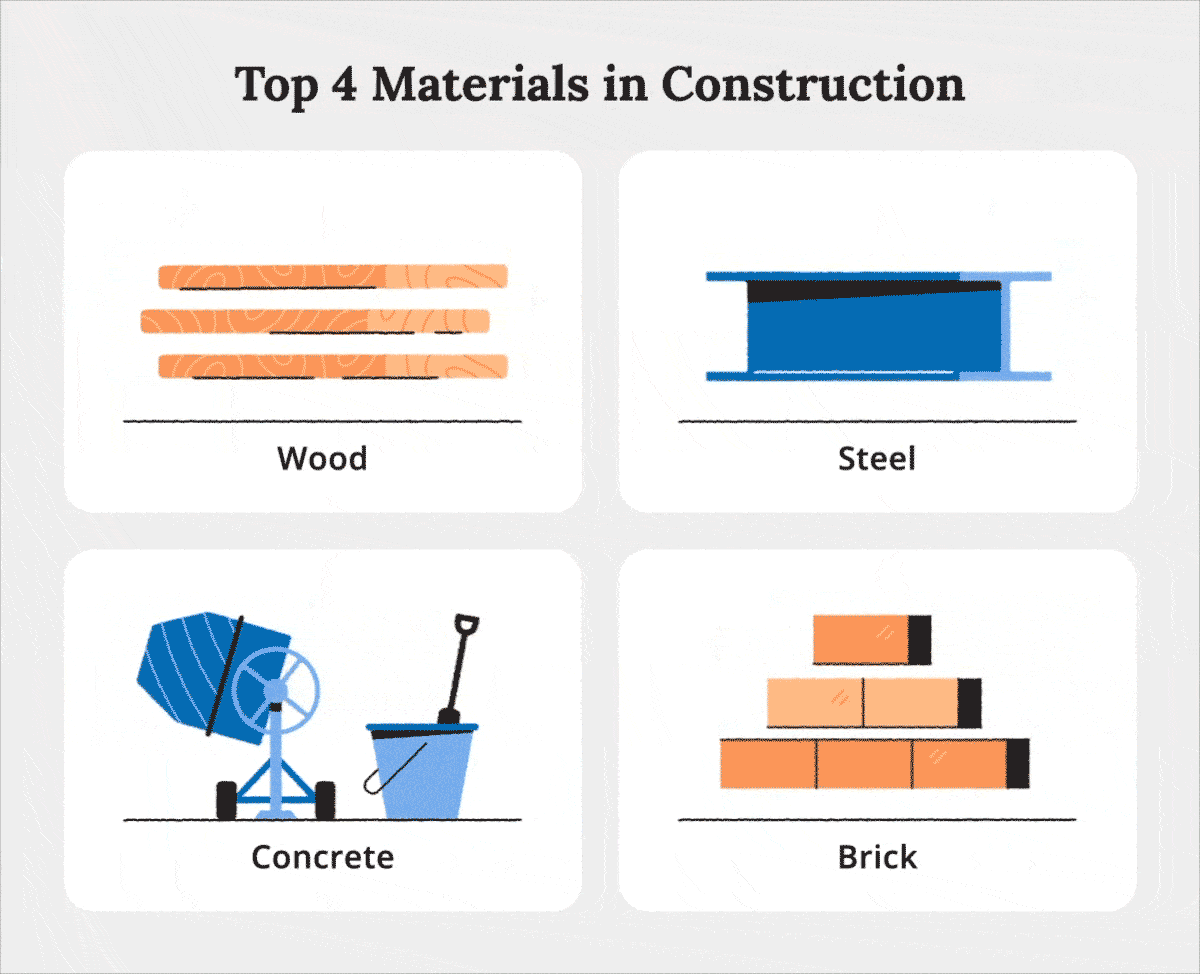
Wood
Using wood—or “timber”—for homes traces back thousands of years, making wood one of the oldest building materials.
Lightweight and a natural resource, wood is readily available and the most commonly used material in construction. Wood is easy to cut and resize, and naturally provides good insulation that comes in handy for living spaces.
Since producing lumber uses less water and energy than other materials, it has a lower carbon footprint. Wood that will be exposed to moisture, however, needs to be pressure-treated to increase its lifespan. If not, it’ll be vulnerable to insects and rot.
If you plan to build in an area prone to wildfires or flooding, wood may not be the best option. Wood also requires more maintenance than other materials, as it can shrink and expand from water absorption if not well-treated.
Best for:
- One- and two-story home frames
- Room extensions
- Walls
- Cabinetry
- Flooring
Steel
As a fusion of carbon and iron, steel is stronger and more resistant to rust and deterioration than traditional metal. Steel has a high strength-to-weight ratio, meaning it can handle heavy weights exceeding its own weight and size.
Another important characteristic of steel is that it doesn’t warp, crack, or split under pressure, making it one of the most durable building materials. Unlike wood, steel is rot- and fire-resistant. For this reason, you can place steel in nearly any environment, and installment is less time-consuming than others.
Malleable and recyclable, steel is a top choice for unique building designs. You can take advantage of its versatility by building sleek and modern garage alternatives, such as carports and storage sheds.
Best for:
- Garages
- Walls
- Multi-story building frames
- Carports
Concrete
While often used for creating concrete slabs and other supporting structures, concrete can also be a useful building material for homes. Like steel, concrete is more durable and resistant to damage than wood and able to withstand more wind, fire, and insects.
Concrete is made of cement, water, and aggregates—particles of sand, rock, and gravel—that bind together and solidify when mixed1. Once hardened, concrete is very low-maintenance. Though concrete will require professional installation, skilled architects can use it to create remarkable designs.
Since concrete holds its shape for decades, its durable form can bear heavy loads and withstand moist soil, which is why many homeowners use it as a solid foundation for basements and garages.
Concrete tends to be more expensive than metal and wood materials, but it can help save money in the long run. This is because concrete creates airtight insulation and absorbs heat, creating an energy-efficient home.
Best for:
- Foundations
- Supporting beams
- Walls
- Garage flooring
Brick
Durable and long-lasting, brick serves as a major building material for historic homes and buildings. Nowadays, it’s increasingly popular as textured exterior siding or covering. You’ll see more brick used for load-bearing walls and pavements, a decorative alternative to concrete.
Building with brick gives you more creative control for structural design since it’s available in various colors, sizes, and patterns. Brick is also fire-, insect-, and water-resistant like steel and concrete. Since brick can help retain heat, it’s great for chimneys and can help make the home more energy efficient.
Despite its creative use, building with brick takes much longer than other materials. Bricks are heavy, and the process of laying and binding them together with mortar prolongs installation time. It will most likely require several laborers to complete construction.
Best for:
- Siding
- Wall covers
- Chimneys
- Driveways
Best Materials for Energy-Efficiency
There are many benefits to building with energy-efficient materials, including fewer drafts, lower energy use, and low maintenance, all of which put more back in your pocket each month.
Most energy-efficient building materials are also sustainable, meaning they’re naturally produced and environmentally friendly to use. While the four common materials above have energy-efficient qualities, not all of them are sustainable.
Below, we explore a few more building materials options that help to conserve energy and preserve the environment.
Recycled Steel
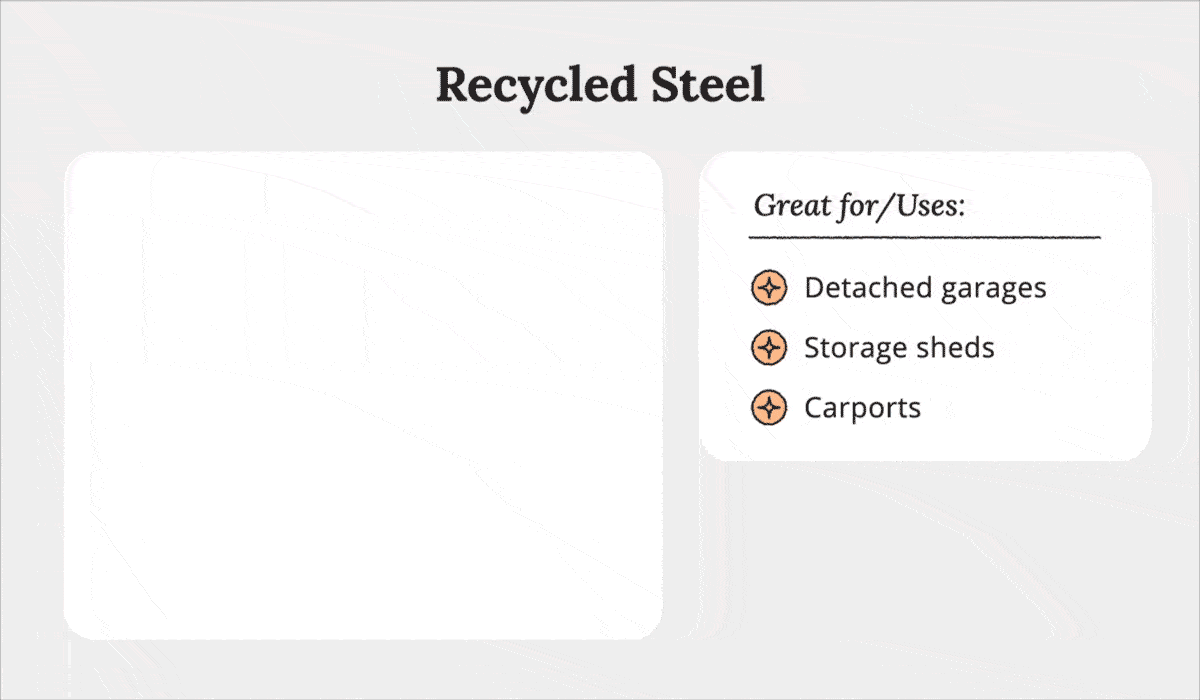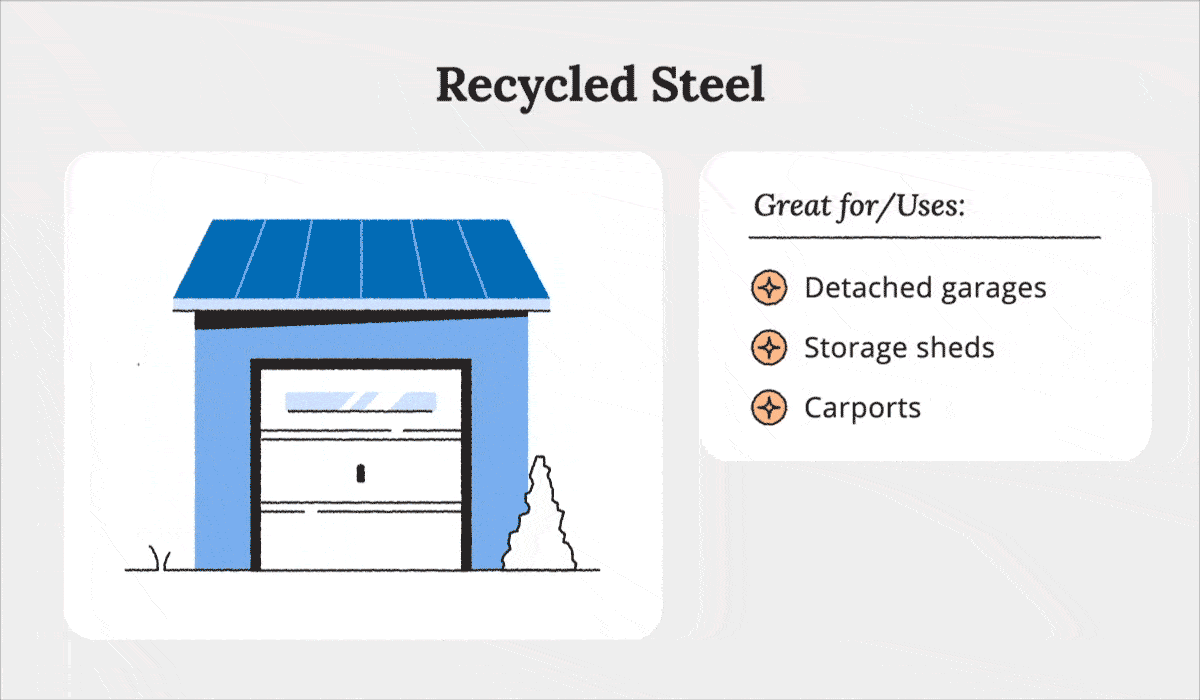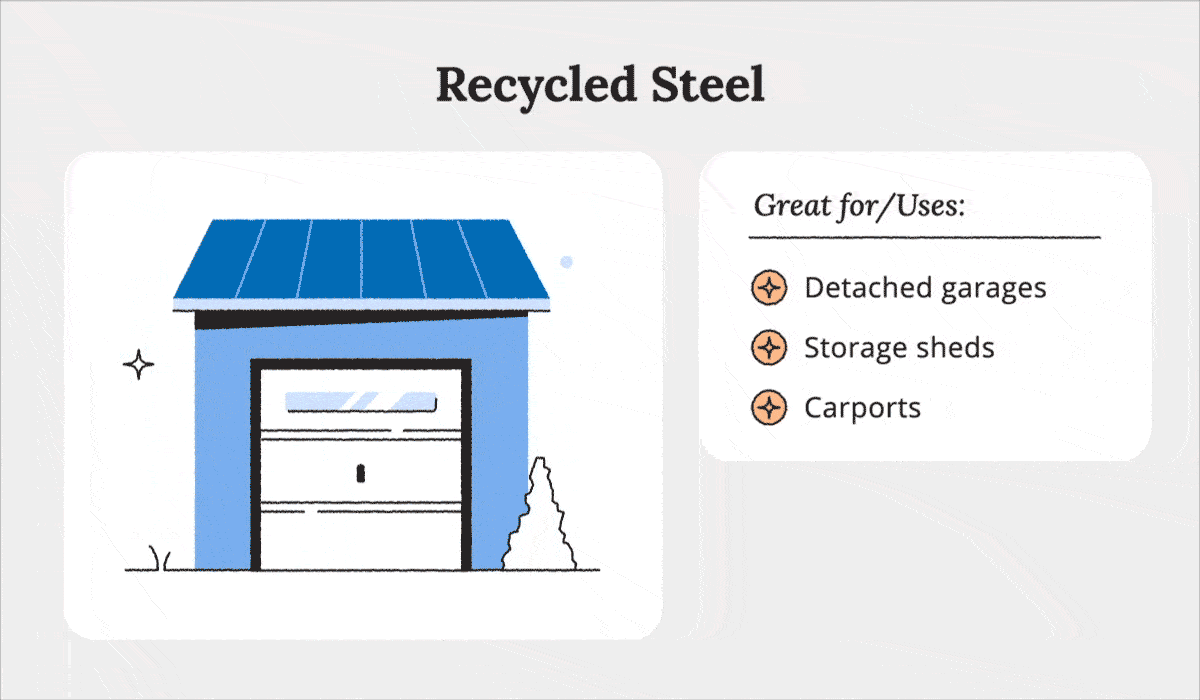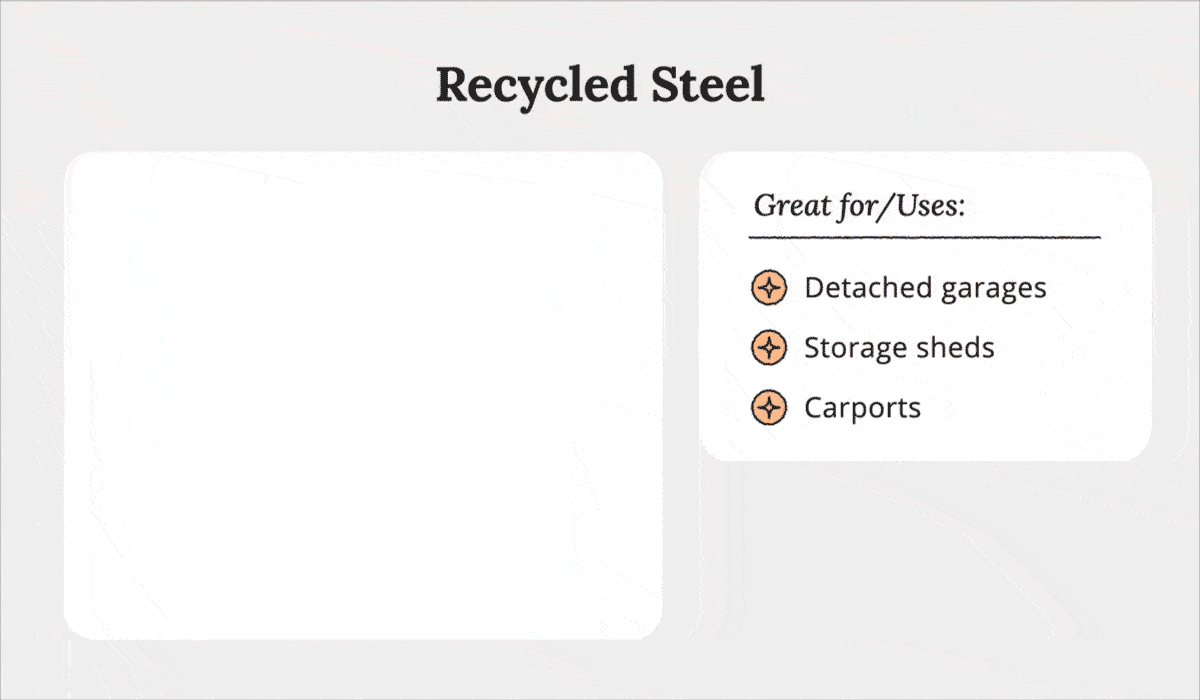
According to the World Steel Association2, steel is the most recycled material in the world. As a recyclable material, you can reuse it for construction. Recycled steel is a little cheaper than standard steel, yet maintains its same durable quality to build it in any location or climate.
Recycled steel structures make for great storage sheds and garages, serving as a protective barrier and shelter for vehicles against wind and weather damage.
Insulated Concrete Forms
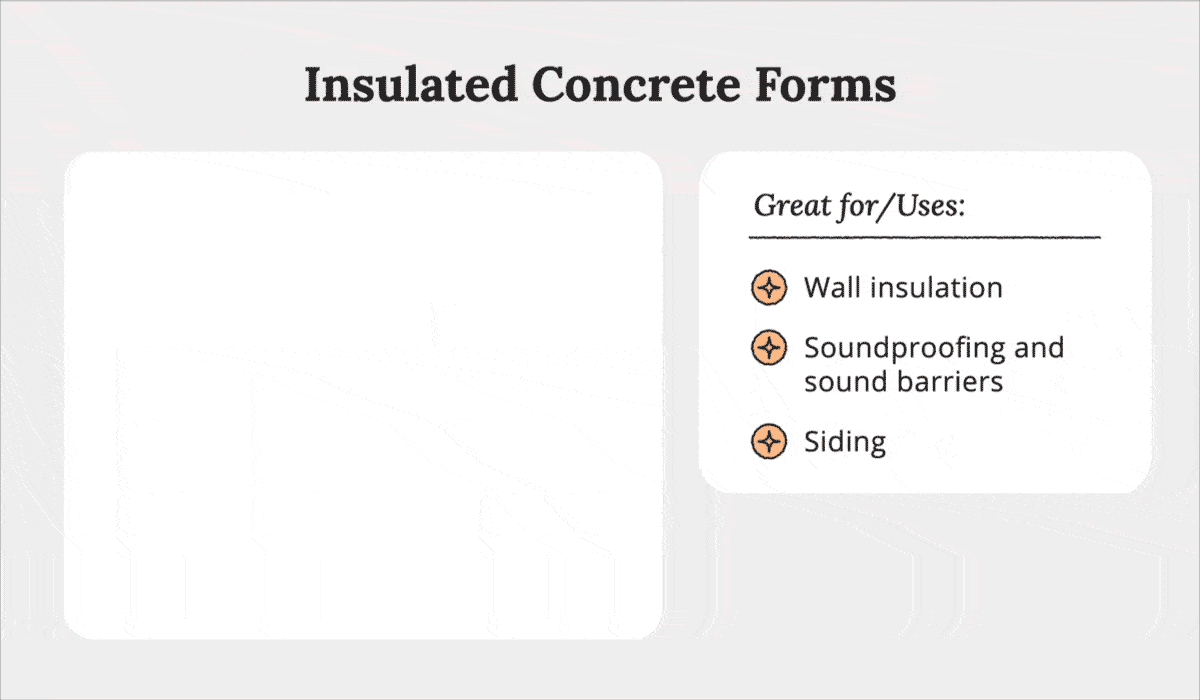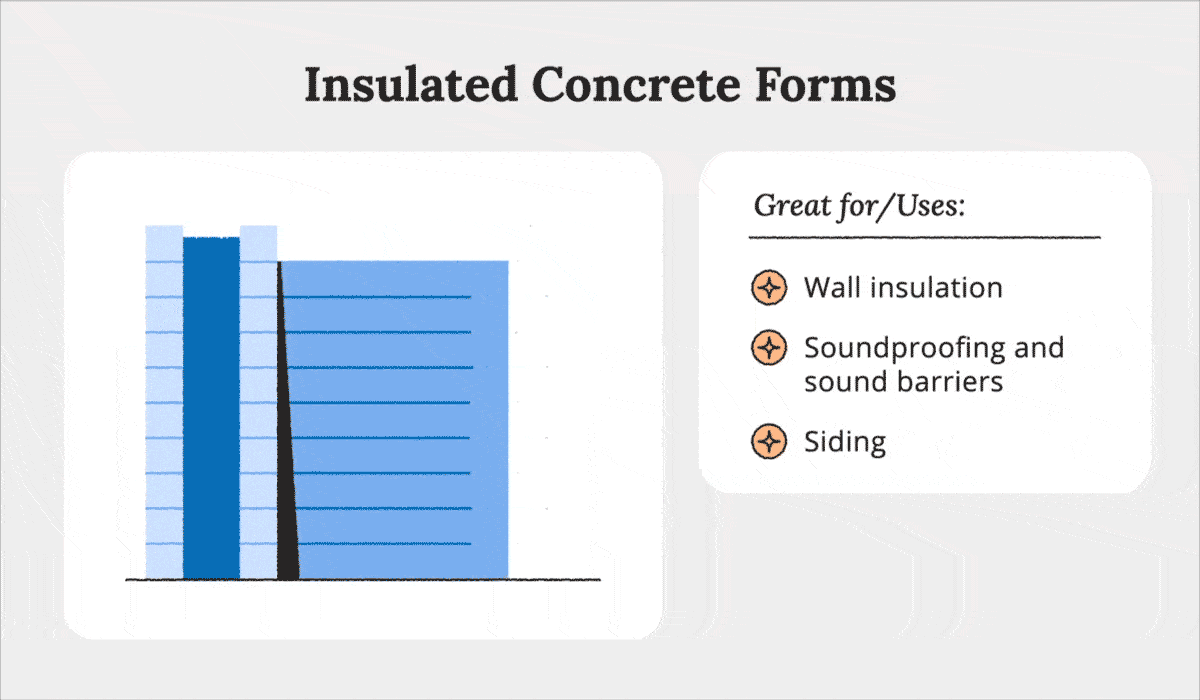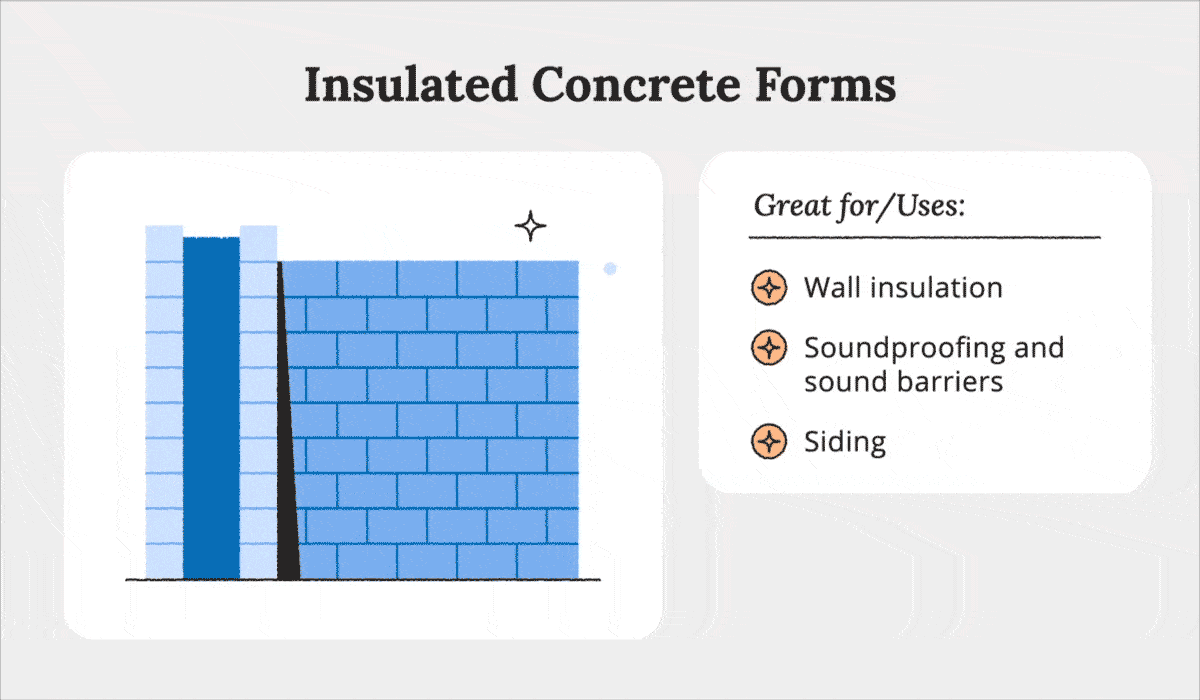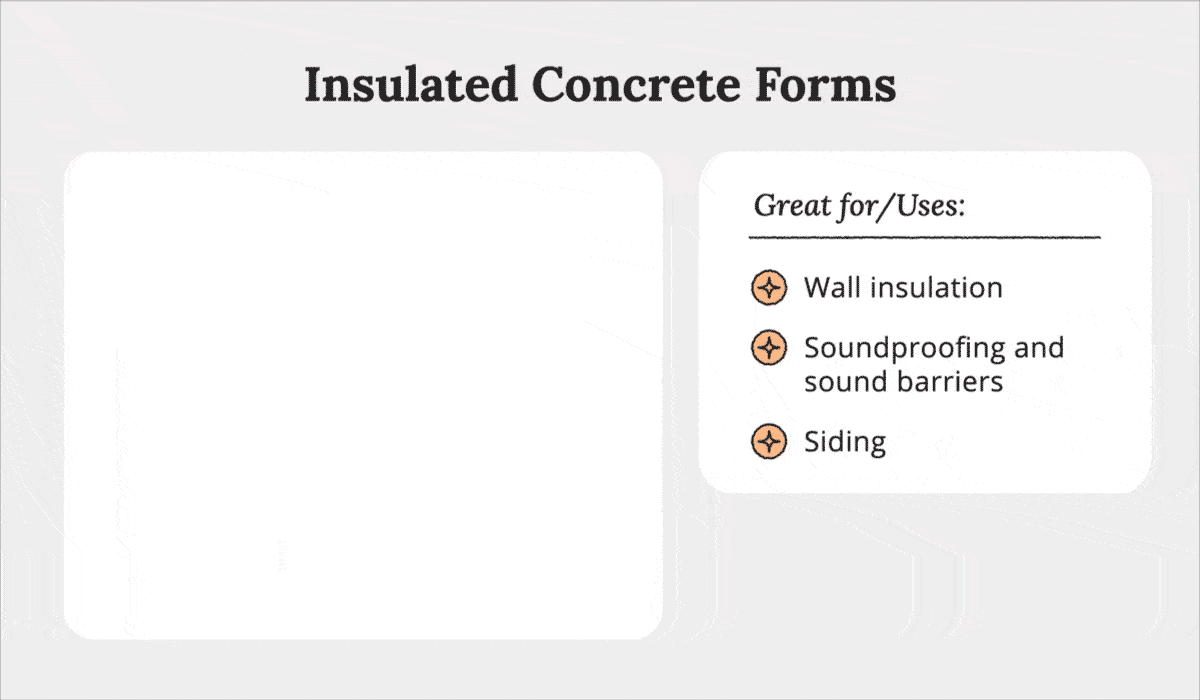
Insulated concrete forms (ICFs) can be described as poured-in-place concrete walls between two thick layers of foam insulation. This “sandwich” form of ICFs creates an airtight seal, or great insulation.
The excellent insulation of ICFs also helps reduce heating and cooling costs, soundproof walls, and even prevent insect and pest infestation. With the same durability as concrete walls, buildings made of ICFs can withstand many natural disasters.
H3: Recycled Wood

Cutting down trees may sound harmful to the environment, but there are eco-conscious alternatives to building with wood: recycled wood. This type of wood comes from responsible timber suppliers who practice sustainable forestry.
Plastic composite lumber, a popular type of material, is lumber mixed with recycled plastic bags. The plastic helps strengthen the lumber and, when merged, are moisture-resistant and less susceptible to mold and rot.
Recycled plastic is more expensive than traditional treated lumber but more durable and long-lasting.
Bamboo Plywood
Bamboo is a fast-growing grass that can imitate wood when used in construction. As a self-regenerating plant, bamboo is a renewable resource that helps reduce carbon emissions.
Bamboo plywood is much stronger than wood and suitable for humid environments. Also, since bamboo replenishes more rapidly than trees, it can be harvested more frequently and readily available.
Bamboo generally costs a little more than wood, but it makes up for the price in quality. Bamboo is naturally pest-resistant, low-maintenance, and known to reduce air pollution.
H3: Rammed Earth

An ancient construction technique, rammed earth has made a comeback in modern, sustainable building practices. Its name is exactly as it sounds: It’s compacted raw materials from the earth like gravel, sand, and clay that solidify to create walls and other structures.
Don’t underestimate the quality of rammed earth. This abundant material is popular around the world, with the Great Wall of China being one of many famous structures made from it.
Since rammed earth is made of 100% natural materials, it’s safe for the environment. It’s also easy to repair and malleable to create various designs.
Rammed earth prices are on the higher end compared to those of other building materials. This is primarily due to the technique rather than the material—you’ll need to hire a craftsman who specializes in building with earth.
Cost Considerations
The average cost of home addition projects is $46,498.3 Weighing the uses and benefits of each building material can help you determine which ones will give the best bang for your buck.
Below are a few considerations to remember when comparing them.
Goals
Before any home construction project, it’s important to have specific goals to meet your needs. Are you adding space? Will you be performing upgrades that make the home more eco-friendly or sustainable? Outline goals to help stay within your budget and avoid unnecessary changes.
Location
The first thing to think about is where you’re planning to build. An area that is prone to natural disasters—wildfires, earthquakes, flooding, etc.—will most likely require more maintenance and repair if not built with durable material like concrete or steel.
Design
The design of your home should improve function, comfort, and convenience. A home more than two stories high will need more load-bearing material, while home extensions like decks and garages will most likely consist of heat-absorbing and temperature-regulating material.
Budget
What’s the project cost limit? A hired professional can help you determine which materials are best for your space without compromising your budget. For example, while energy-efficient materials tend to cost more upfront, they can help save money down the line.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are building materials so expensive?
Building materials are expensive primarily due to inflation and supply shortages, both of which affect the costs. Shipping costs, which fluctuate depending on gas prices, can also influence material costs.
What is the most durable building material?
Steel is the most durable building material when comparing its size and weight to its load-bearing capacity. That said, all four common building materials—wood, concrete, brick, and steel—are long-lasting and can reinforce one another to strengthen any structure.
How can I save on construction costs?
Reducing the square footage of your home design is a strategic way that can help you save on construction costs. For example, instead of having an attached garage, you can opt for a prefabricated detached garage, which costs less and is quicker to build.
Get an Estimate for Your Next Project
If you’re trying to save money on your home construction, building a detached garage is a low-cost alternative to an attached version. Our residential steel buildings can serve a garage, storage shed, workshop space, and more.
Use our 3D tool below to custom-design a detached space made of durable, recyclable steel.
Sources
- “Cement & Concrete Basics FAQs,” n.d. Sourced February 23, 2023. https://www.cement.org/cement-concrete/cement-and-concrete-basics-faqs.
- B. Greenhalgh. “How Much Does a Home Addition Cost to Build?” July 29, 2022. https://www.bobvila.com/articles/home-addition-cost/
- Worldsteel. “Steel Core Green Economy. – Worldsteel.Org.” worldsteel.org, February 9, 2023. https://worldsteel.org/about-steel/steel-industry-facts/steel-core-green-economy/.