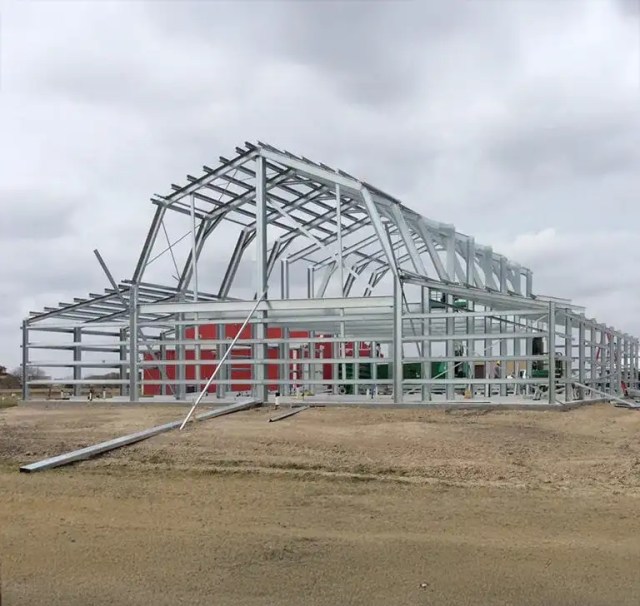
If you’re planning a new metal building, understanding your options is one of the most critical steps in the process. Two of the most common types are tubular metal buildings and cold-formed steel buildings, and while they may seem similar on the surface, they serve very different purposes.
Tubular metal buildings are typically made with lightweight steel tubing and bolt-together frames. They’re cost-effective, easy to assemble, and widely used for prefab garages, carports, and basic shelters.
Cold-formed steel buildings, on the other hand, are engineered from roll-formed steel components and designed for strength, longevity, and code compliance. These structures use a rigid steel frame and are better suited for larger, more complex building projects.
Knowing the strengths and limitations of each building type helps homeowners, DIYers, and commercial developers make informed decisions. Whether you’re choosing based on price, performance, or long-term adaptability, the right option depends on your goals, site conditions, and timeline.
This guide breaks down how tubular and cold-formed steel buildings compare — covering costs, durability, lead times, and project fit — so you can confidently move forward with the right structure for your needs.
What Are Tubular Metal Buildings?
Tubular metal buildings are structures constructed using lightweight steel tubing as the primary framing material. These tubes are typically galvanized to resist rust and corrosion, making them suitable for long-term outdoor use. Unlike rigid steel frame systems, tubular buildings often feature a bolt-together design that simplifies the assembly process for homeowners and DIYers.
This building type shows up frequently in small-scale projects like carports, garages, sheds, and workshops. It’s affordable, easy to install, and doesn’t need much of a foundation, which makes it a popular choice in rural and suburban areas. Prefab kits are widely available, making shipping simpler and cutting down project time.
Characteristics of tubular metal buildings include:
- Tube frame construction. The structure relies on square or rectangular steel tubing, typically 14- or 12-gauge, for vertical supports and horizontal framing.
- Bolt-together design. Components are pre-cut and drilled, allowing for straightforward on-site assembly with basic tools.
- Cost-effective materials. Tubular steel costs less than heavier hot-rolled alternatives, making it a value choice for light-duty applications.
- DIY accessibility. These buildings are commonly sold in prefab kits ideal for homeowner-led installation projects.
While tubular buildings provide excellent value for garages and carports, they may not offer the same structural strength as cold-formed or red iron steel options for larger or more demanding building projects.
What Are Cold-Formed Metal Buildings?
Cold-formed metal buildings use sheet steel shaped at room temperature through roll-forming or press-braking. This process produces lightweight, strong framing with solid load-bearing strength, making these steel structures both efficient and durable. Unlike tubular buildings that use hollow steel tubing, cold-formed buildings use C- or Z-shaped channels built for structural performance.
These steel frame systems are becoming more common in residential and light commercial builds because of their strength, versatility, and ability to meet modern building codes. You’ll see them in barndominiums, small warehouses, agricultural storage, and large garages. Since they’re precision-engineered, they’re often used for clear-span layouts and taller walls than tubular options.
Notable features of cold-formed steel buildings include:
- Engineered steel frame components. The framing members are made from galvanized steel sheets and formed into structural shapes such as C-channels or Z-purlins.
- Superior structural integrity. Cold-forming increases the steel’s strength-to-weight ratio, which enhances durability without added bulk.
- Versatile applications. These buildings are ideal for projects needing higher wind/snow ratings or more complex design features.
- Prefab and code-ready. Kits are often prefabricated and designed to meet local building codes, simplifying permitting and inspection processes.
Cold-formed buildings offer a strong middle ground between tubular and red iron steel structures. They provide the strength and engineering support necessary for more demanding applications while remaining lighter and more cost-effective than hot-rolled options.
Material and Structural Differences
When comparing metal building types, the core difference often comes down to the materials used — and how those materials affect structure, strength, and longevity.
Tubular buildings are constructed using hollow steel tubing, typically galvanized for corrosion resistance. These tubes are lightweight and easy to handle, which makes them ideal for smaller structures like carports and garages. However, they’re limited in load-bearing strength.
Cold-formed steel buildings use roll-formed steel channels engineered for structural performance. These components strike a balance — they’re stronger than tubular options but still relatively lightweight. That makes them well-suited for both residential and light commercial buildings.
Red iron buildings, also called hot-rolled steel buildings, are made with I-beams and heavy-duty structural steel. These materials are thicker, heavier, and designed to handle significant loads. Red iron steel is often fire-resistant and corrosion-resistant, especially when galvanized, making it a top choice for warehouses, large garages, and industrial facilities.
Here’s a quick comparison of the material and structural properties of each type:
| Steel Building Type Comparison | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Building type | Weight | Corrosion resistance | Structural capacity |
| Tubular steel | Lightweight | Good (galvanized) | Limited to small structures |
| Cold-formed steel | Moderate weight | Very good (galvanized) | High for its weight |
| Red iron steel | Heavy duty | Excellent (fire-resistant) | Maximum load-bearing |
Choosing between these materials depends on your specific project needs — from building size and purpose to weather exposure and local code requirements.
Durability and Performance
Durability plays a significant role in deciding which metal building type is right for your project, especially in areas with high-wind conditions or heavy snow loads. Whether you’re building in a region with severe weather or long-term sun exposure, it’s important to know how each structure type holds up over time:
- Tubular steel buildings are lightweight and easy to install. They’re suitable for small structures in mild climates but don’t have the same structural integrity as other types.
- Cold-formed steel buildings provide strong all-around performance. Their engineered frames handle wind and snow well, making them a reliable choice for most residential and light commercial projects.
- Red iron steel buildings deliver top-tier durability. With heavy-duty materials and natural fire resistance, they’re built for high-demand environments and long-term use.
| Durability by Steel Building Type | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance factor | Tubular buildings | Cold-formed steel buildings | Red iron buildings |
| Wind and snow resistance | Moderate; limited by lighter frames. Best in low wind/snow areas | Strong; engineered to meet higher wind and snow load ratings | Excellent; ideal for extreme climates and consistent high-wind exposure |
| Corrosion protection | Good; galvanized steel resists rust | Very good; galvanized with consistent protective coatings | Excellent; often includes thicker steel and extra protective layers |
| Fire resistance | Dependent on coatings | Dependent on coatings | Naturally fire-resistant |
| Lifespan and maintenance | May require more upkeep over time | Low maintenance; built to last decades | Very low maintenance; highly durable over time |
Each of these steel structures brings different strengths to the table. The right choice depends on your location, intended use, and expectations for long-term performance.
Design Flexibility and Versatility
When planning a building project, design flexibility matters — especially if you’re trying to balance layout, functionality, and future use. Use the Metal Building Designer at Alan’s Factory Outlet to explore layout options, adjust dimensions, and see how different features impact your building’s functionality and cost.
Here’s how tubular and cold-formed steel buildings compare across key design features.
Clear-Span Potential
Tubular buildings have limited clear-span capabilities. Their lightweight frames support smaller widths and are best for single-use layouts like carports or basic garages. Cold-formed buildings, by contrast, support wide clear-span designs with no interior columns. This makes them ideal for open interiors in garages, workshops, hangars, and even small manufacturing facilities.
Interior Layout Options
Tubular buildings typically use fixed, simple floor plans and aren’t well-suited for structural changes or room divisions. Cold-formed buildings offer far more versatility, with flexible framing that can support complex layouts, partitioned spaces, and hybrid residential or commercial applications like barndominiums or manufacturing facilities.
Mezzanines and Lofts
Tubular buildings generally can’t support mezzanines or lofts due to structural limitations. Cold-formed buildings, on the other hand, can be engineered to accommodate vertical space expansions like mezzanines, which increases both adaptability and interior function.
Customization Potential
Tubular kits offer basic customization in size and color, with limited add-ons such as doors or windows. Cold-formed kits provide significantly more flexibility, allowing for custom openings, lean-tos, varied roof pitches, and other layout-specific features. These are often designed in collaboration with a building designer.
If your project requires more than a basic shelter, cold-formed buildings have the adaptability and design flexibility needed to tailor the space to your goals.
Price and Lead Times
Cost and delivery time make a big difference when deciding between tubular and cold-formed steel buildings. While both come in prefab kits, they differ in price, lead time, and installation.
Not sure which is a better fit for your needs or budget? Try the Metal Building Designer at Alan’s Factory Outlet to compare pricing and customize your layout in minutes.
Price Comparison
Tubular buildings are generally more cost-effective. They use lighter materials and simpler construction methods, which helps keep manufacturing and delivery costs down. This makes them a budget-friendly choice for smaller projects like carports or garages.
Cold-formed steel buildings tend to cost more up front due to their engineered components and added strength. However, their durability and long-term value often justify the higher initial investment — especially for larger or more demanding building projects.
Lead Times
Tubular kits often have shorter lead times. Because many are manufactured in standard sizes and kept in stock, they can be shipped quickly after ordering.
Cold-formed buildings typically require longer lead times. Their custom engineering and higher material demands mean additional production time, especially if the building must meet specific local code requirements.
DIY-Friendliness
Tubular buildings are popular among DIYers. Their bolt-together design and lighter frames make them easy to assemble with basic tools without the need for a professional.
Cold-formed kits are still DIY-friendly for experienced builders but require more planning and coordination. Some projects may benefit from professional assistance, particularly if custom features or site prep are involved.
Impact of Prefab Kits
Both tubular and cold-formed buildings are available as prefab kits, which helps reduce construction time and simplifies the building process. Tubular kits are often more streamlined, while cold-formed kits allow more customization to fit specific needs and site conditions.
Compliance With Building Codes
Meeting local building codes is a critical step in any construction project — especially when safety, insurance, and permitting are on the line. The type of metal building you choose plays a big role in whether your structure will meet local requirements.
Tubular Buildings and Code Limitations
Tubular buildings are often not engineered to meet local area codes or specific load-bearing standards. Because they use bolt-together tubing and standardized kits, they typically don’t come with certified engineering documents. In some cases, they can be upgraded to meet code, but doing so adds time and cost to the project.
These structures are best suited for simpler uses — like carports or storage buildings — in low-risk zones where structural certification isn’t strictly required.
Cold-Formed Buildings and Code Compliance
Cold-formed steel buildings are often built with code compliance in mind from the start. Their engineered steel frames are designed to handle wind, seismic, and snow loads based on local conditions. They can be customized to meet or exceed the structural requirements laid out by state and municipal codes.
This makes cold-formed buildings a reliable choice for permanent residential or commercial installations — especially in areas where code enforcement is strict.
Choosing the Right Fit
If you’re building in a zone with high wind, heavy snow, or strict inspection processes, tubular kits might not qualify without major modification. Cold-formed (and in many cases, red iron) buildings are often required for compliance — and offer the structural integrity needed for long-term performance.
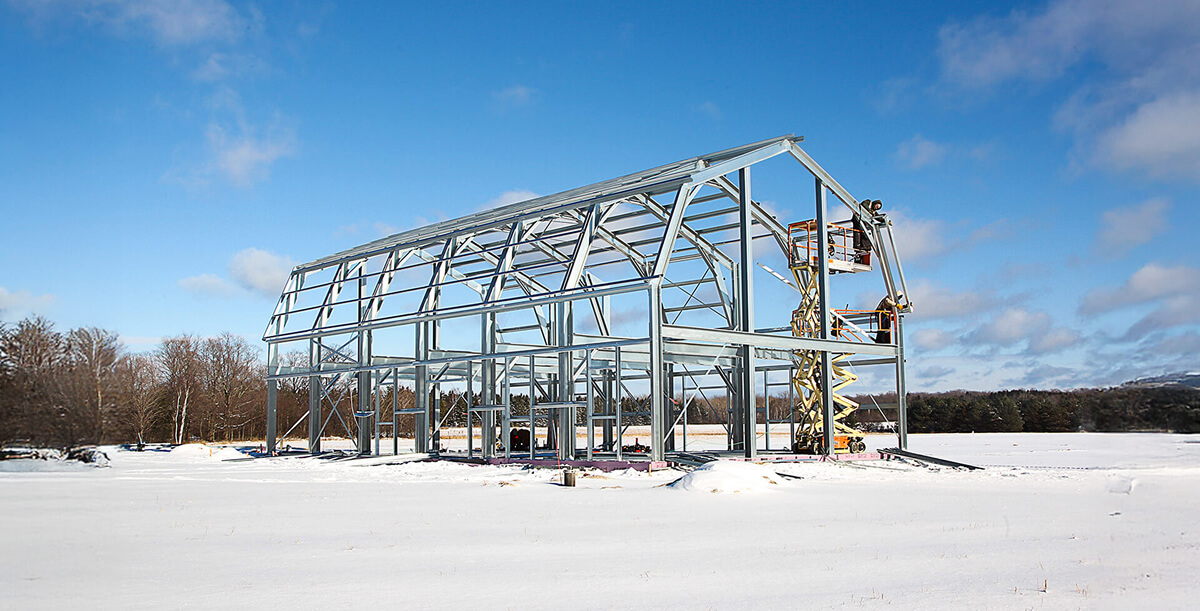

Which Is Right for Your Project?
Choosing the right building type depends on your goals, location, and budget. Both tubular and cold-formed steel structures offer unique benefits depending on the scope of your building project. Tubular buildings are great for smaller setups like carports, simple garages, and equipment shelters — especially in mild climates. They’re more affordable and easier to install, making them a strong option for straightforward needs.
Cold-formed buildings offer more flexibility for larger or more complex projects. They work well for hangars, workshops, or residential-style garages, especially in areas with strict building codes or where high-wind and snow load requirements apply. Their engineering backs long-term durability and supports custom designs.
To find the right fit, start by looking at your main priorities:
- Intended use. Are you building a basic carport or something more involved, like a workshop, garage, or living space?
- Building size and layout. Larger footprints and open interiors often require stronger framing and more design flexibility.
- Local codes and permitting. Cold-formed buildings are more likely to meet on-site building code requirements, especially in regulated areas.
- Budget. Tubular buildings are generally more cost-effective up front, while cold-formed kits may offer better long-term value.
- Wind and snow ratings. Consider your local climate. Cold-formed structures are typically better equipped to handle extreme weather conditions.
- Timeline and installation. Tubular kits are faster to install and DIY-friendly; cold-formed kits may require more planning or professional support.
For help choosing the right metal building for your property, visit Alan’s Factory Outlet to compare kits, get a free quote, and explore on-site options tailored to your location.
FAQs About Metal Building Types
When deciding between tubular and cold-formed steel buildings, many buyers have similar questions. Below are quick answers to some of the most common concerns.
What is the difference between red iron and cold-formed steel?
Red iron buildings use hot-rolled I-beams for maximum structural strength, making them ideal for large industrial buildings. Cold-formed steel buildings, by contrast, use lighter roll-formed components and are engineered for residential and light commercial use.
Are tubular steel buildings durable in harsh weather?
Tubular buildings can withstand moderate conditions but aren’t typically engineered for high-wind or heavy snow areas. For demanding climates, cold-formed or red iron buildings offer stronger structural integrity.
Can I build a tubular garage without a contractor?
Yes. Tubular buildings are designed for easy, on-site assembly and are popular with DIYers thanks to their bolt-together frames and lightweight materials.
Do cold-formed buildings meet all U.S. building codes?
They often do, especially when ordered with proper engineering documentation. Cold-formed kits are customizable to meet wind, snow, and seismic code requirements for your location.
Which metal building is best for DIYers?
Tubular buildings are typically the easiest option for DIY installation. Cold-formed kits can also be DIY-friendly but may require more time, tools, and preparation.